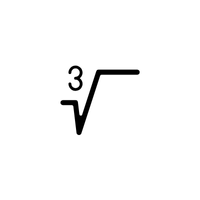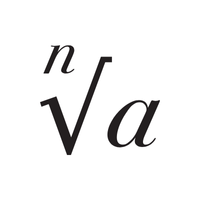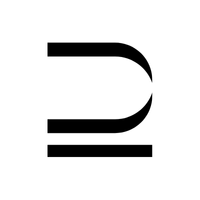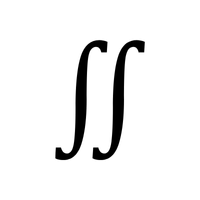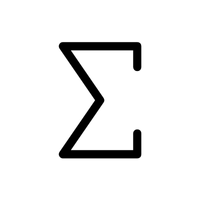All Math Symbols Names in English
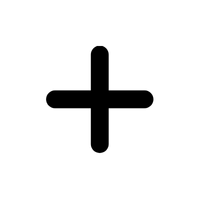
- Plus (+)
- Minus (−)
- Multiplication (× or *)
- Division (÷ or /)
- Equals (=)
- Not Equal (≠)
- Approximate (≈)
- Identical To (≡)
- Greater Than (>)
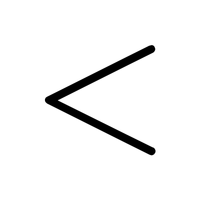
- Less Than (<)
- Greater Than or Equal To (≥)
- Less Than or Equal To (≤)
- Variable (x, y, z)
- Parentheses ( )
- Brackets [ ]
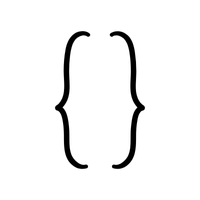
- Braces { }
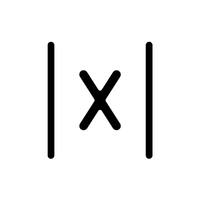
- Absolute Value (|x|)
- Plus-Minus (±)
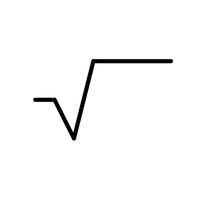
- Square Root (√)
- Cube Root (∛)
Useful List of Mathematical Symbols with Pictures
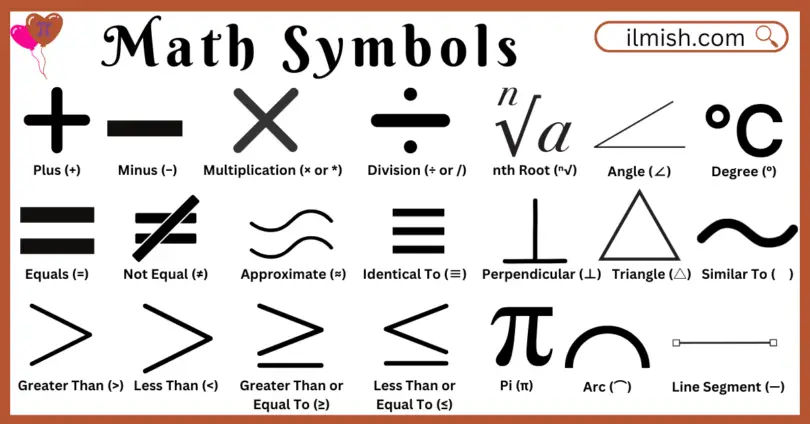
- Plus (+)
Used for addition to combine two numbers or values.

- Minus (−)
Represents subtraction, removing one number from another.

- *Multiplication (× )
Shows repeated addition of a number.

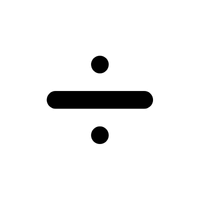
- Division (÷ or /)
Splits a number into equal parts.

- Equals (=)
Indicates that two values are the same.

- Not Equal (≠)
Means two values are not the same.

- Approximate (≈)
Shows that a value is close but not exact.

- Identical To (≡)
Represents equal values that are always the same.

- Greater Than (>)
Shows that one number is larger than another.

- Less Than (<)
Indicates that one number is smaller than another.

- Greater Than or Equal To (≥)
Means a value is either greater or the same.

- Less Than or Equal To (≤)
Indicates a value is smaller or equal.

- Variable (x, y, z)
Symbols that represent unknown numbers.

- Parentheses ( )
Group parts of an equation to show priority.

- Brackets [ ]
Used inside parentheses for clarity in equations.
![Brackets [ ] | Math Symbols names in English](data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciIHdpZHRoPSIyMDAiIGhlaWdodD0iMjAwIiB2aWV3Qm94PSIwIDAgMjAwIDIwMCI+PHJlY3Qgd2lkdGg9IjEwMCUiIGhlaWdodD0iMTAwJSIgc3R5bGU9ImZpbGw6I2NmZDRkYjtmaWxsLW9wYWNpdHk6IDAuMTsiLz48L3N2Zz4=)
- Braces { }
Used for sets or grouping multiple elements.

- Absolute Value (|x|)
Represents the distance of a number from zero.

- Plus-Minus (±)
Shows both positive and negative possibilities.

- Square Root (√)
finds a number that equals the specified integer when multiplied by itself.

- Cube Root (∛)
Finds a number that, when multiplied three times by itself, equals the given number.

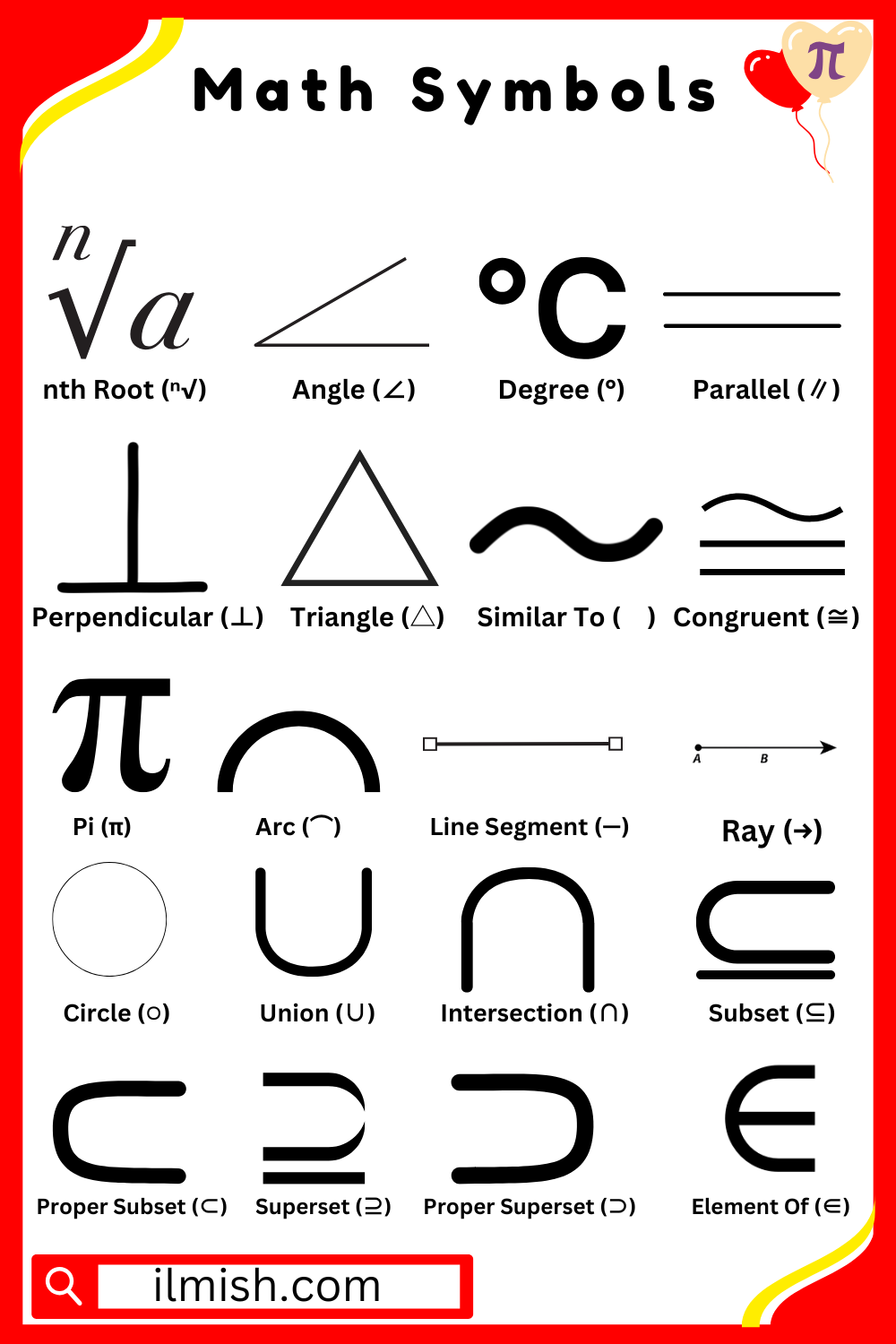
List of math symbols names
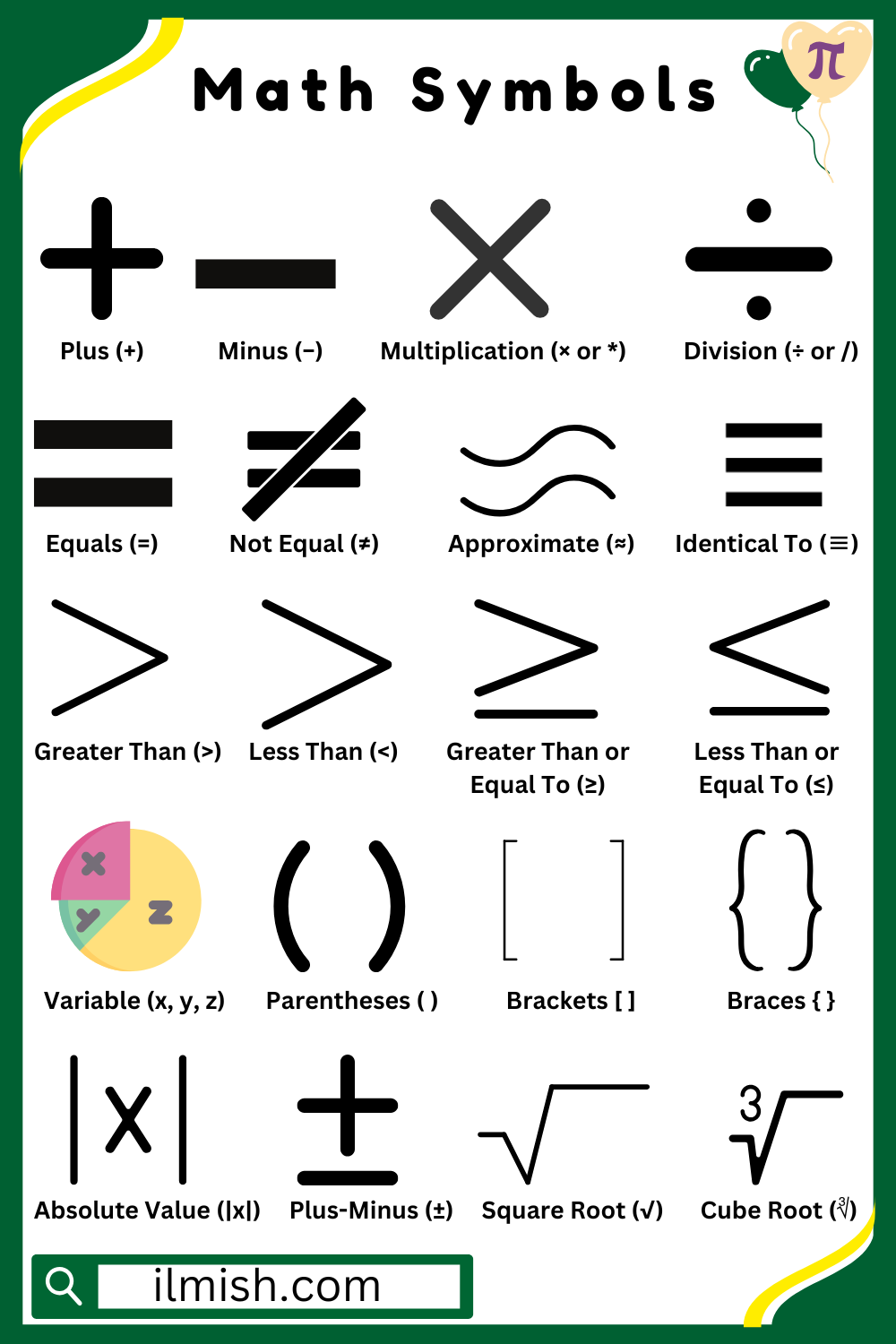
- nth Root (ⁿ√)
- Angle (∠)
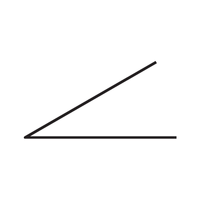
- Degree (°)
- Parallel (∥)
- Perpendicular (⊥)
- Triangle (△)
- Similar To (∼)
- Congruent (≅)
- Pi (π)
- Arc (⌒)
- Line Segment (—)
- Ray (→)
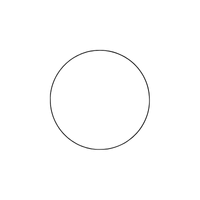
- Circle (○)
- Union (∪)
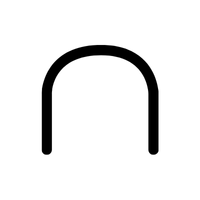
- Intersection (∩)
- Subset (⊆)
- Proper Subset (⊂)
- Superset (⊇)
- Proper Superset (⊃)
- Element Of (∈)
All Mathematical Symbols with Pictures
- Nth Root (ⁿ√)
Finds a number that, when raised to the nth power, gives the original number.

- Angle (∠)
two lines that come together to form a shape.

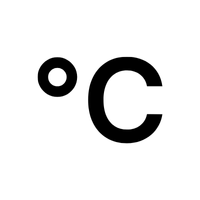
- Degree (°)
Measures the size of an angle.

- Parallel (∥)
lines that remain the same distance apart and never meet.

- Perpendicular (⊥)
Two lines that come together at a 90° right angle.

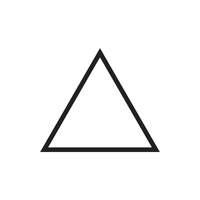
- Triangle (△)
A shape with three sides and three angles.

- Similar To (∼)
Indicates that two shapes have the same shape but different sizes.

- Congruent (≅)
Shows that two shapes have the same size and shape.

- Pi (π)
A constant (3.14159…) used in circle calculations.

- Arc (⌒)
A curved part of a circle.

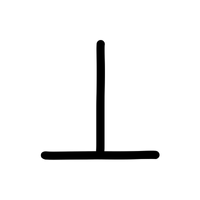
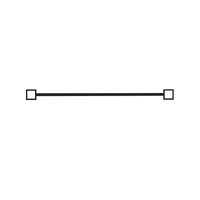
- Line Segment (—)
A straight path with two endpoints.

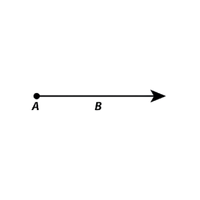
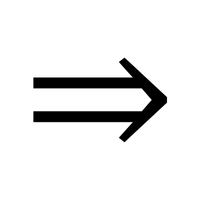
- Ray (→)
A straight path that starts at a point and extends forever in one direction.

- Circle (○)
a circular form in which every point is equally spaced from the center.

- Union (∪)
Combines all elements from two sets.

- Intersection (∩)
Finds common elements between two sets.

- Subset (⊆)
A set that is completely inside another set.

- Proper Subset (⊂)
A set that is inside another but not equal to it.

- Superset (⊇)
a set with every element from another set in it.

- Proper Superset (⊃)
A larger set that contains another set but is not equal to it.

- Element Of (∈)
Shows that an item belongs to a set.

Useful Mathematical Symbols and their Names
- Not an Element Of (∉)
- Empty Set (∅)
- Percentage (%)
- Per Mille (‰)
- Proportional To (∝)
- Decimal Point (.)
- Sine (sin)
- Cosine (cos)
- Cotangent (cot)
- Secant (sec)
- Cosecant (csc)
- Integral (∫)
- Double Integral (∬)
- Triple Integral (∭)
- Partial Derivative (∂)
- Delta (Δ)
- Nabla (∇)
- Limit (lim)
- Summation (Σ)
- Infinity (∞)
Math symbols names in English and their pictures
- Not an Element Of (∉)
Shows that an item does not belong to a set.

- Empty Set (∅)
A set with no elements inside it.

- Percentage (%)
Represents a number out of 100.

- Per Mille (‰)
Represents a number out of 1,000.

- Proportional To (∝)
Shows a relationship where one value changes with another.

- Decimal Point (.)
Separates the whole number from the fractional part.

- Sine (sin)
A trigonometric function related to the opposite side of an angle in a right triangle.

- Cosine (cos)
A trigonometric function related to the adjacent side of an angle in a right triangle.

- Secant (sec)
A trigonometric function, the reciprocal of cosine.

- Cosecant (csc)
A trigonometric function, the reciprocal of sine.

- Integral (∫)
Represents the area under a curve in calculus.

- Double Integral (∬)
Used to calculate volume in a two-dimensional space.

- Triple Integral (∭)
Used to calculate volume in a three-dimensional space.

- Partial Derivative (∂)
Shows how a function changes with respect to one variable while keeping others constant.

- Delta (Δ)
Represents a change or difference in a value.

- Nabla (∇)
Represents gradient, divergence, or curl in vector calculus.

- Limit (lim)
Describes the value a function approaches as input gets closer to a point.

- Summation (Σ)
Represents the sum of multiple values.

- Infinity (∞)
Represents an endless or unbounded quantity.

Mathematical symbols list
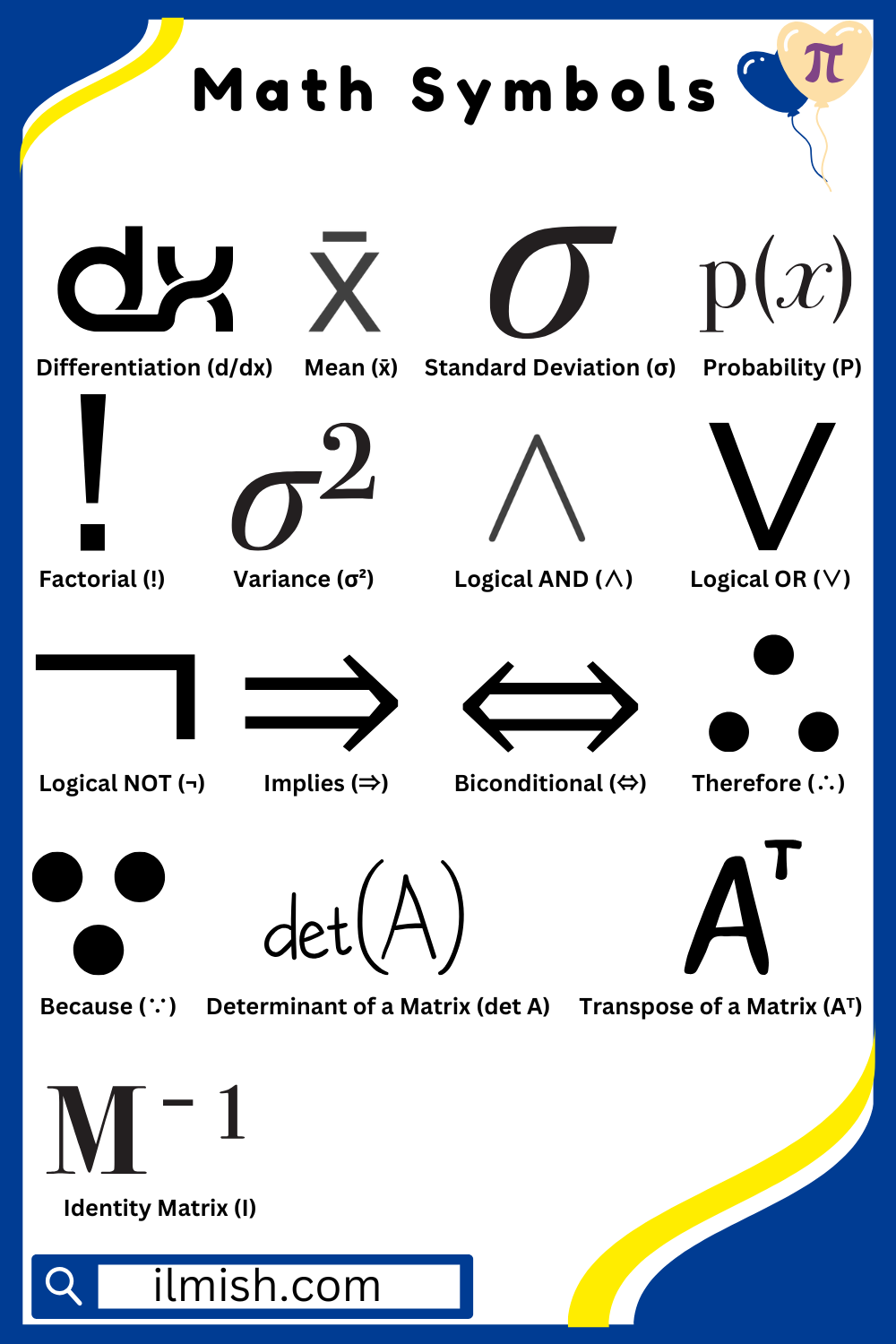
- Differentiation (d/dx)
- Mean (x̄)
- Standard Deviation (σ)
- Probability (P)
- Factorial (!)
- Variance (σ²)
- Logical AND (∧)
- Logical OR (∨)
- Logical NOT (¬)
- Implies (⇒)
- Biconditional (⇔)
- Therefore (∴)
- Because (∵)
- Determinant of a Matrix (det A)
- Transpose of a Matrix (Aᵀ)
- Identity Matrix (I)
80 mathematical symbols with their Pictures
- Differentiation (d/dx)
Represents the rate of change of a function with respect to a variable.

- Mean (x̄)
The average value of a set of numbers.

- Standard Deviation (σ)
Measures how much data values vary from the mean.

- Probability (P)
Represents the likelihood of an event happening.

- Factorial (!)
The product of all whole numbers from 1 to a given number.

- Variance (σ²)
Measures how spread out numbers are in a data set.

- Logical AND (∧)
True if both conditions are true.

- Logical OR (∨)
True if at least one condition is true.

- Logical NOT (¬)
Reverses the truth value of a statement.

- Implies (⇒)
Shows that one statement leads to another.

- Biconditional (⇔)
Means two statements are true or false together.

- Therefore (∴)
Indicates a conclusion based on previous statements.

- Because (∵)
Shows the reason behind a conclusion.

- Determinant of a Matrix (det A)
A special number used to analyze a matrix.

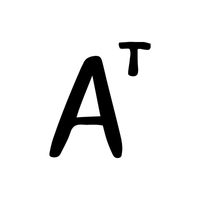
- Transpose of a Matrix (Aᵀ)
Flips a matrix over its diagonal.

- Identity Matrix (I)
A square matrix with 1s on the diagonal and 0s elsewhere.

Learn more helpful article



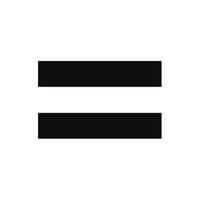


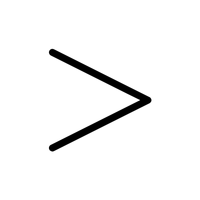
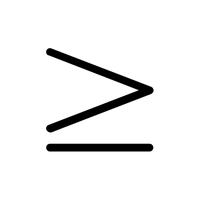
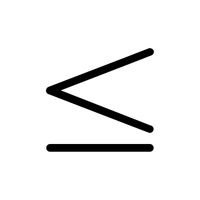

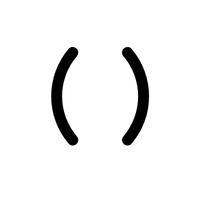
![Brackets [ ] | Math Symbols names in English](https://ilmish.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Brackets-.png)