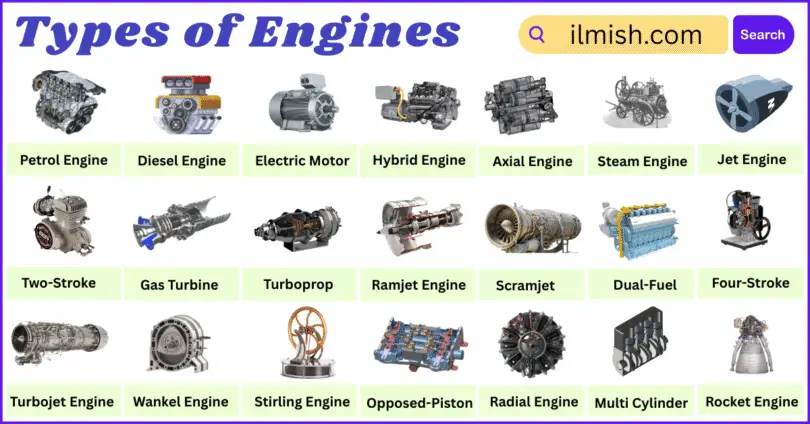
Types of Engines Names in English
- Petrol Engine
- Diesel Engine
- Two-Stroke Engine
- Four-Stroke Engine
- Electric Motor
- Hybrid Engine
- External Combustion Engine
- Steam Engine
- Gas Turbine Engine
- Jet Engine
- Turbojet Engine
- Turbofan Engine
- Turboprop Engine
- Ramjet Engine
- Scramjet Engine
- Rocket Engine
- Wankel Engine (Rotary Engine)
- Stirling Engine
- Opposed-Piston Engine
- Radial Engine
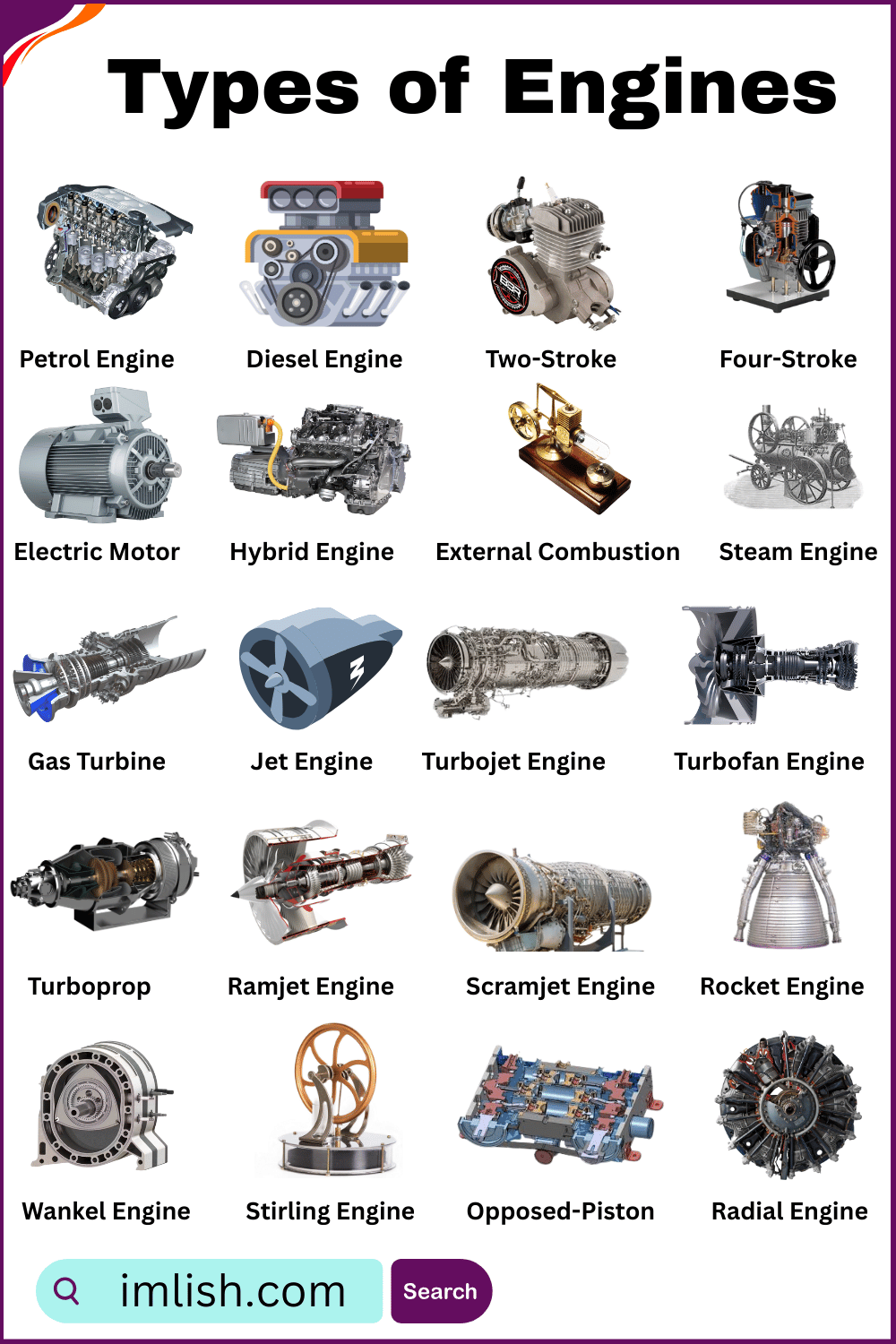
Types of Engines Names in English with Pictures
- Petrol Engine
An engine that uses petrol (gasoline) as fuel to make power for cars or bikes.

- Diesel Engine
A strong engine that runs on diesel fuel, mostly used in trucks, buses, and big machines.

- Two-Stroke Engine
A simple engine that completes a power cycle in two steps, often found in bikes and small tools.

- Four-Stroke Engine
A common engine that works in four steps to produce power, used in most cars and motorcycles.

- Electric Motor
A machine that uses electricity instead of fuel to move vehicles like electric cars and scooters.

- Hybrid Engine
A smart engine that uses both fuel and electricity to save energy and reduce pollution.

- External Combustion Engine
An engine where fuel burns outside the engine to create power, like in steam engines.

- Steam Engine
An old engine that uses steam from boiling water to move trains or machines.

- Gas Turbine Engine
A powerful engine that burns gas to spin a turbine and create fast movement, used in planes.

- Jet Engine
A fast engine that throws out hot air to push airplanes forward.

- Turbojet Engine
A type of jet engine that moves air through the engine quickly to fly fast jets.

- Turbofan Engine
A quiet and fuel-efficient jet engine used in most passenger airplanes.

- Turboprop Engine
A jet engine that also spins a propeller, used in small aircraft.

- Ramjet Engine
A jet engine that works at high speed without moving parts, often used in missiles.

- Scramjet Engine
A very fast jet engine that works only at supersonic speeds, used in space research.

- Rocket Engine
A powerful engine that works in space by pushing gas out very fast.

- Wankel Engine (Rotary Engine)
A small and smooth engine that uses a spinning shape instead of pistons.

- Stirling Engine
An engine that uses hot and cold air to move, known for being quiet and efficient.

- Opposed-Piston Engine
An engine with two pistons in one cylinder working against each other to make power.

- Radial Engine
A round engine with many pistons placed in a circle, mostly used in old airplanes.

Engine Name in English
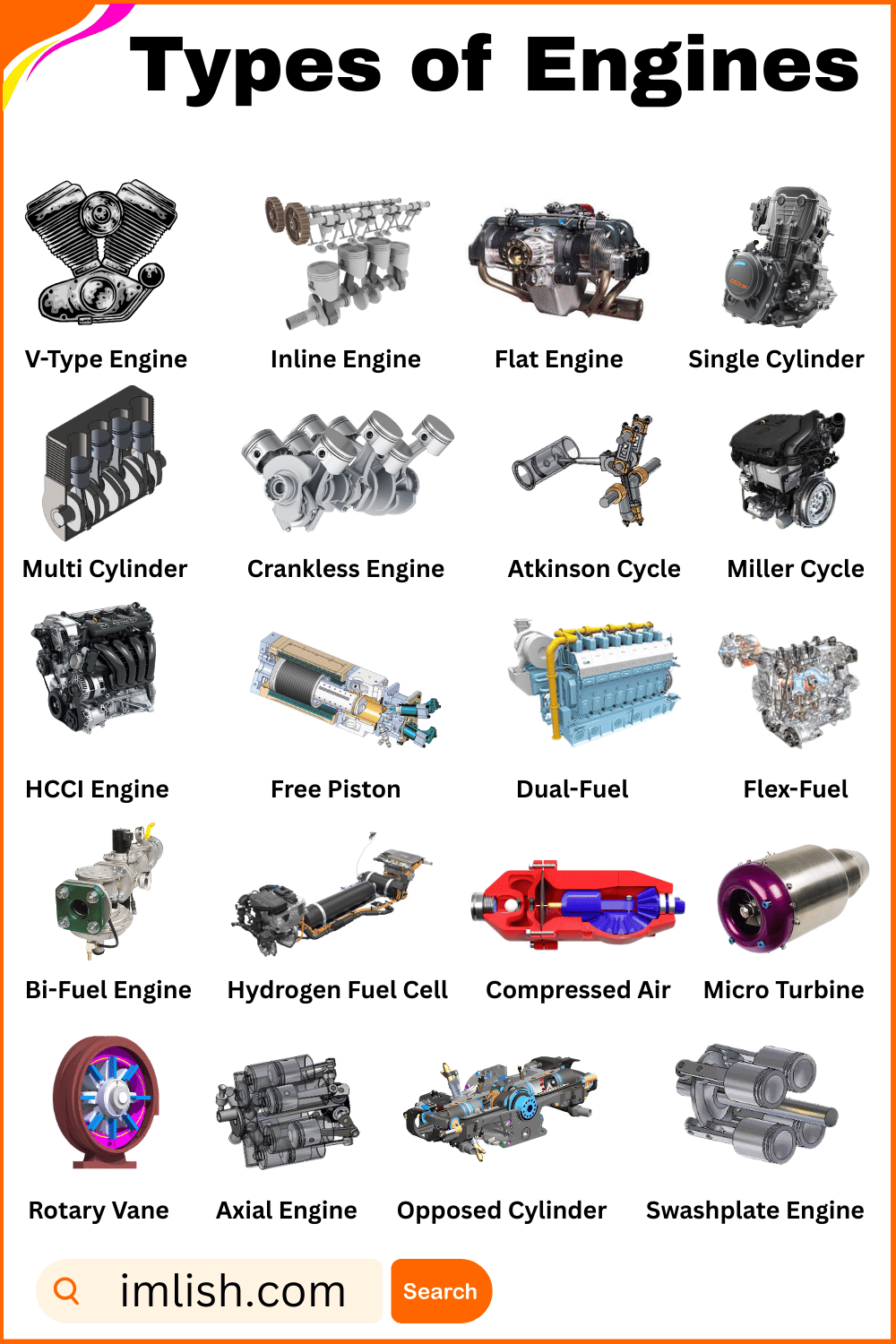
- V-Type Engine
- Inline Engine
- Flat Engine (Boxer Engine)
- Single Cylinder Engine
- Multi Cylinder Engine
- Crankless Engine
- Atkinson Cycle Engine
- Miller Cycle Engine
- HCCI Engine (Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition)
- Free Piston Engine
- Dual-Fuel Engine
- Flex-Fuel Engine
- Bi-Fuel Engine
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Engine
- Compressed Air Engine
- Micro Turbine Engine
- Rotary Vane Engine
- Axial Engine
- Opposed Cylinder Engine
- Swashplate Engine
Types of Engines list in English with Pictures
- V-Type Engine
An engine with cylinders arranged in a “V” shape, often used in powerful cars and trucks.

- Inline Engine
An engine where all cylinders are placed in a straight line, commonly found in many cars.

- Flat Engine (Boxer Engine)
An engine with cylinders lying flat and opposite each other, known for smooth running.

- Single Cylinder Engine
A small engine with only one cylinder, mostly used in scooters, bikes, and lawnmowers.

- Multi Cylinder Engine
An engine with more than one cylinder, giving more power and smoother performance.

- Crankless Engine
A rare engine that works without a crankshaft, using other methods to create motion.

- Atkinson Cycle Engine
A fuel-saving engine used in hybrid cars, designed to improve efficiency.

- Miller Cycle Engine
An engine similar to Atkinson but with better air control, used to reduce fuel use.

- HCCI Engine (Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition) – A modern engine that mixes petrol and diesel ideas for cleaner burning.

- Free Piston Engine
An engine without a crankshaft where pistons move freely to produce power.

- Dual-Fuel Engine
An engine that runs on two types of fuel at the same time, often diesel and gas.

- Flex-Fuel Engine
An engine that can run on more than one type of fuel like petrol or ethanol.

- Bi-Fuel Engine
An engine that can use two fuels, but only one at a time, like petrol and natural gas.

- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Engine
An eco-friendly engine that makes electricity from hydrogen gas and gives off only water.

- Compressed Air Engine
An engine that uses air stored under pressure to move the vehicle.

- Micro Turbine Engine
A small, lightweight engine that spins at high speed to produce power.

- Rotary Vane Engine
An engine that uses rotating vanes inside a housing to create power without pistons.

- Axial Engine
An engine where pistons move along the same line as the shaft, making it compact and powerful.

- Opposed Cylinder Engine
An engine with cylinders set opposite each other in a flat layout for balance.

- Swashplate Engine
A rare engine that uses a tilted plate to move pistons in a compact design.

Learn more helpful articles